Introduction
In the world of serverless computing, AWS Lambda has become a popular choice for executing code without the need for provisioning or managing servers. One of the key features of AWS Lambda is its ability to run functions in response to various events. However, there are scenarios where you may want to offload time-consuming or asynchronous tasks to a background process. In this blog post, we’ll explore how to achieve efficient background processing in AWS Lambda using Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS).
Understanding the Problem
When dealing with serverless architectures, it’s essential to consider the execution time limits imposed by Lambda. Long-running tasks or operations that require more time than the Lambda timeout can become a challenge.
The Solution
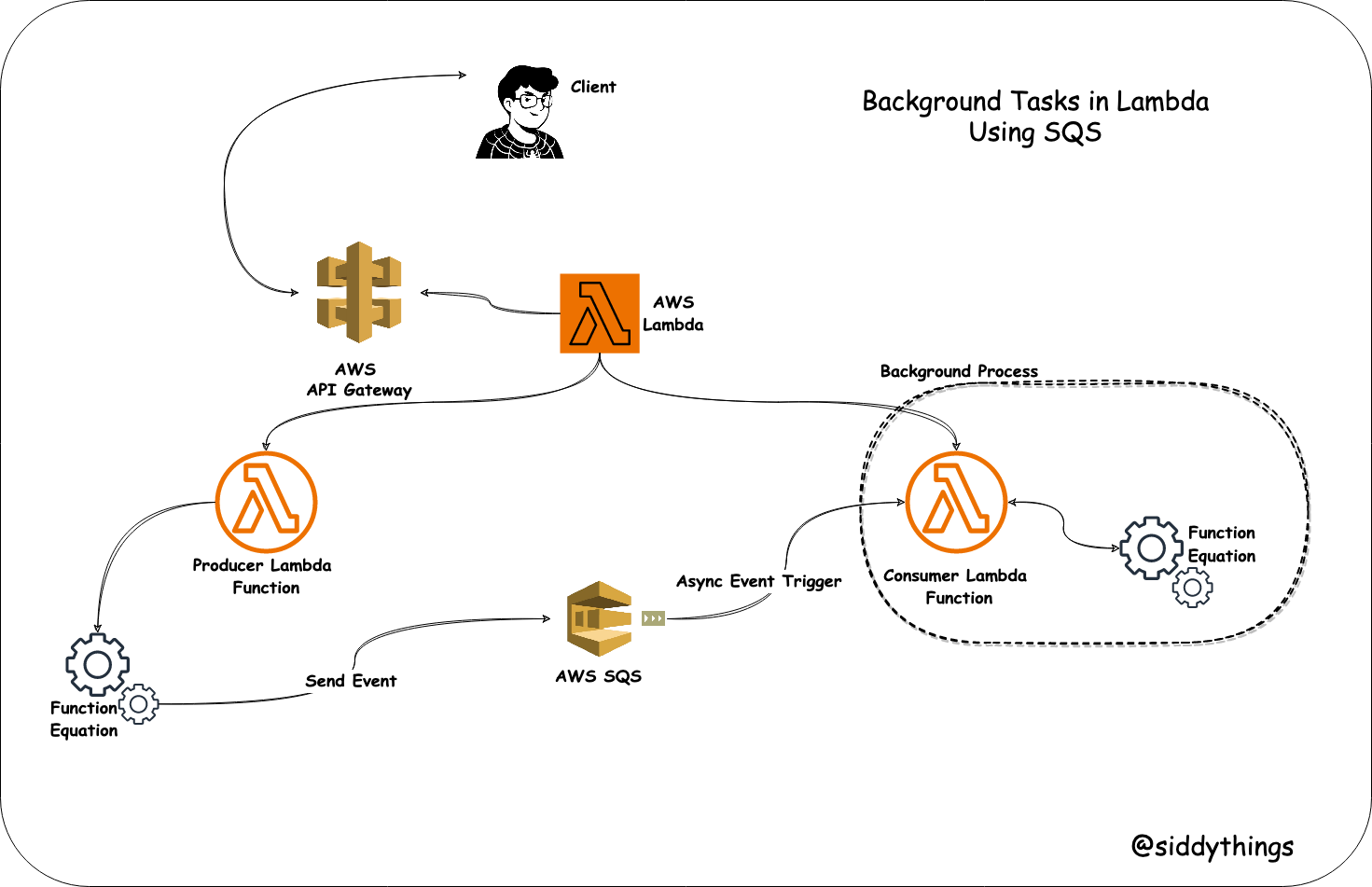 This is where SQS comes into play, allowing you to decouple your Lambda function from the time-consuming task by placing it in a queue.
This is where SQS comes into play, allowing you to decouple your Lambda function from the time-consuming task by placing it in a queue.
Benefits of Using SQS with Lambda
Scalability: SQS provides a scalable and reliable message queuing service, ensuring that messages are delivered between distributed components of cloud applications.
Asynchronous Processing: By integrating SQS with Lambda, you can trigger the Lambda function to process messages from the queue asynchronously, allowing for more extended processing times.
Loose Coupling: SQS promotes loose coupling between different components of your serverless architecture. The Lambda function that places messages in the queue is decoupled from the function processing those messages, providing flexibility and independence.
Implementation Steps
Create Lambda Functions:
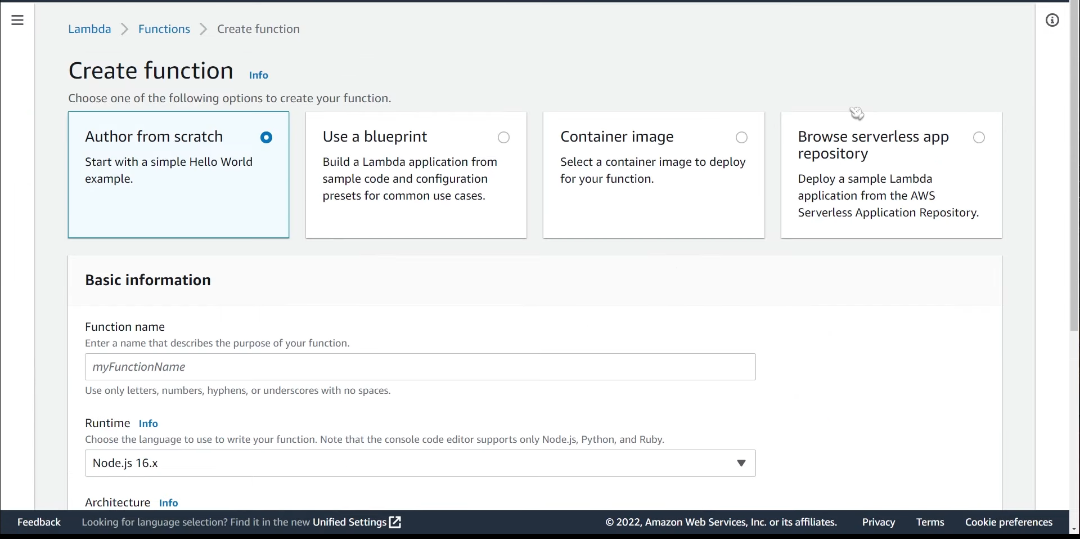
Producer Lambda Function: This Lambda function will be responsible for placing messages in the SQS queue. It is triggered by an event, such as an API Gateway request or an S3 bucket event.Consumer Lambda Function: This Lambda function will be triggered by the SQS queue. It processes the messages, performing the background task.Set Up an SQS Queue:
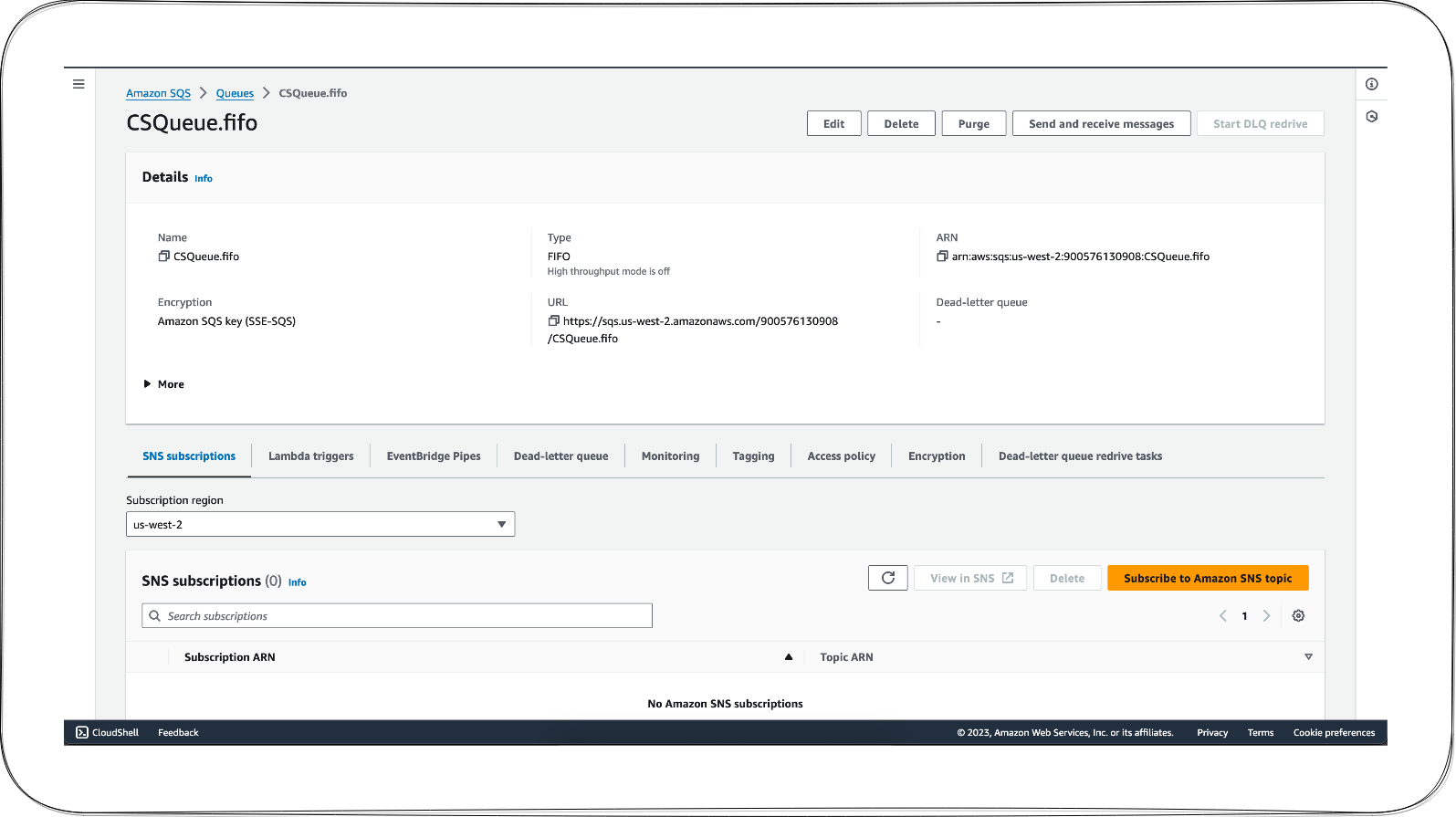 Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to the SQS service.
Create a new standard queue that will act as the communication channel between the Lambda function and the background process.
Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to the SQS service.
Create a new standard queue that will act as the communication channel between the Lambda function and the background process.Configure Lambda Triggers:
 Set up the trigger for the producer Lambda function based on the event that initiates the background processing.
Set up the trigger for the producer Lambda function based on the event that initiates the background processing.
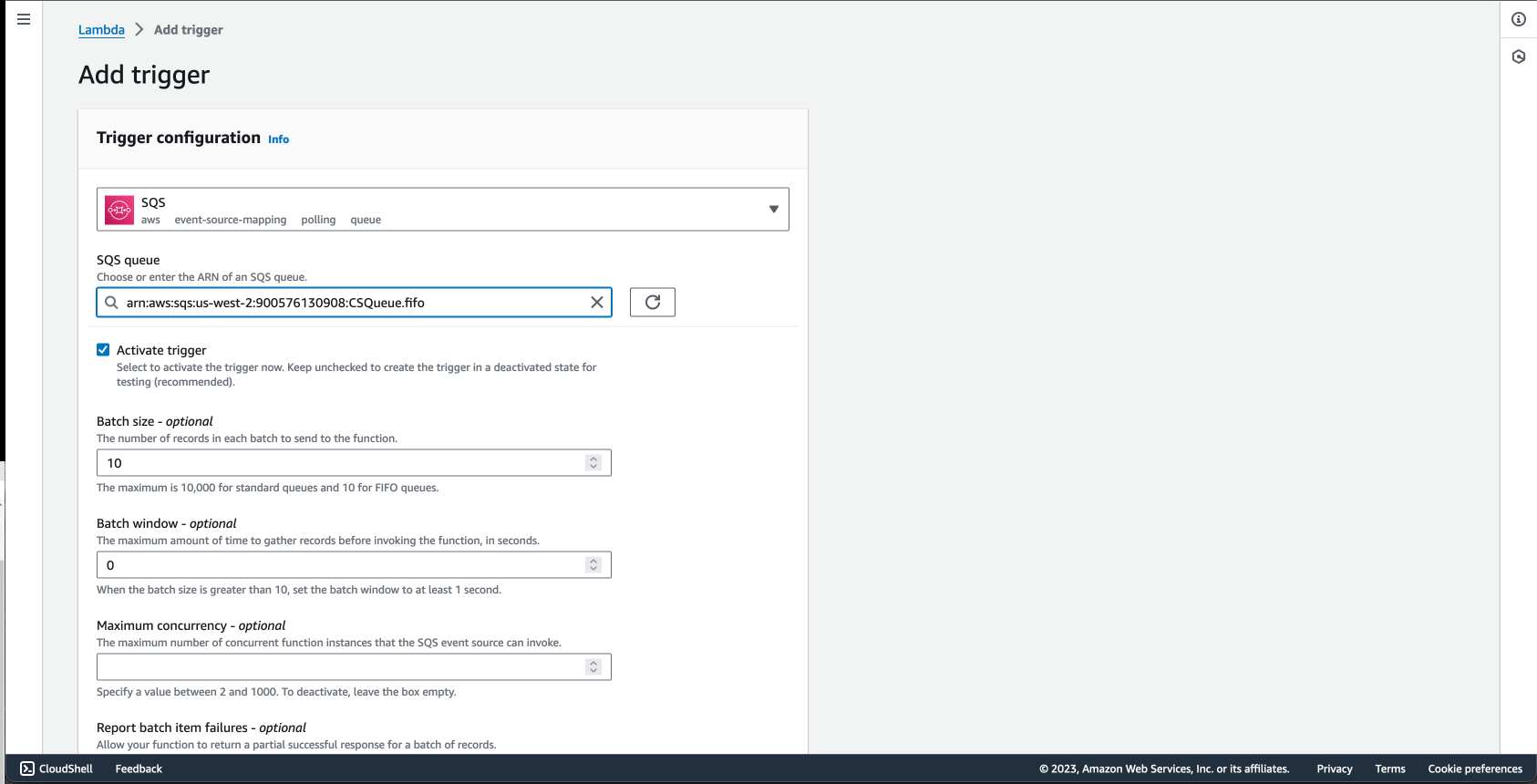 Configure the SQS queue as a trigger for the consumer Lambda function, ensuring that it processes messages from the queue.
Configure the SQS queue as a trigger for the consumer Lambda function, ensuring that it processes messages from the queue.Handling Errors and Retries:
Implement error handling mechanisms within the consumer Lambda function. Configure Dead Letter Queues (DLQs) in SQS to capture messages that cannot be processed successfully after a certain number of retries.
Monitoring and Logging:
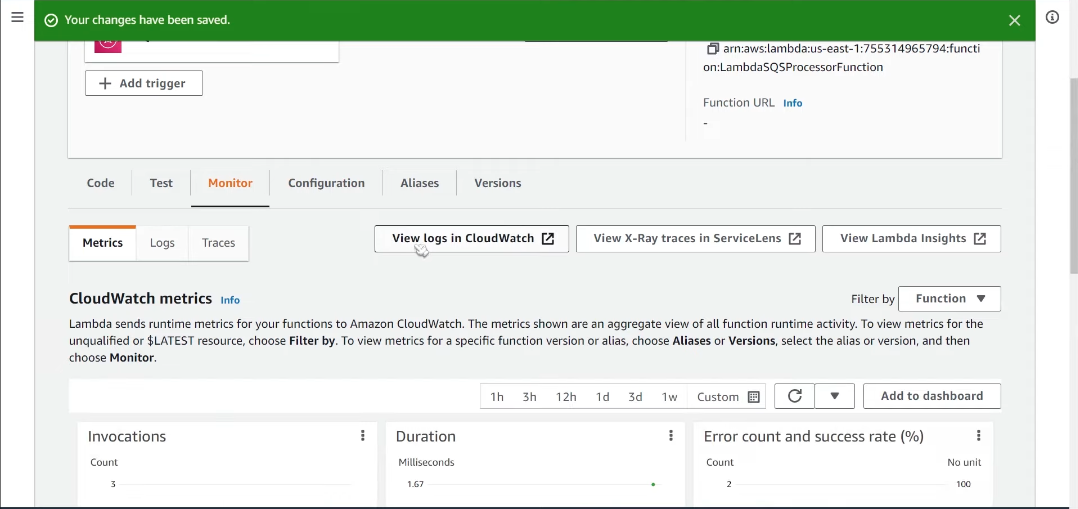 Use AWS CloudWatch Logs and CloudWatch Alarms to monitor the performance and health of your Lambda functions and SQS queues. Implement logging within your functions to capture relevant information.
Use AWS CloudWatch Logs and CloudWatch Alarms to monitor the performance and health of your Lambda functions and SQS queues. Implement logging within your functions to capture relevant information.
With integrating AWS Lambda and SQS, you can achieve efficient background processing in a serverless architecture. This approach allows you to handle long-running tasks, decouple components, and build scalable and reliable systems. As you embark on implementing background processing using SQS and Lambda, consider the specific requirements of your application and tailor the configuration accordingly for optimal performance and reliability.